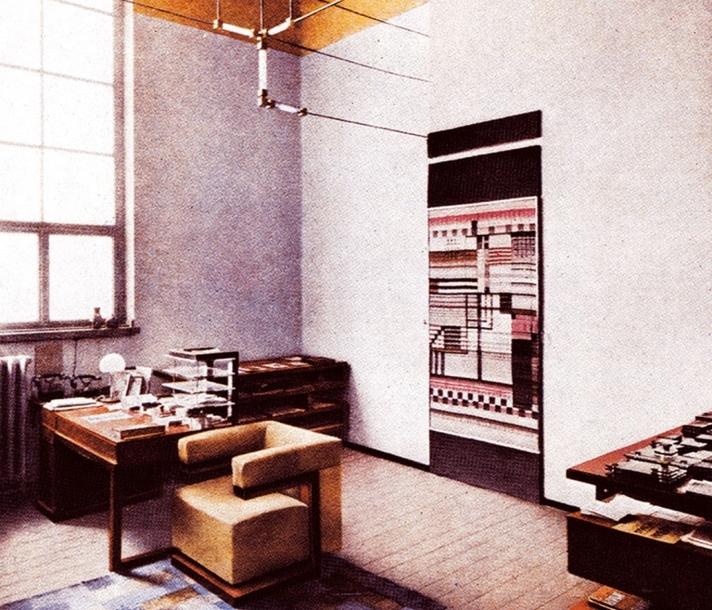
..."Bauhaus Ecologies" at the Bauhaus Museum, Dessau, Germany The Bauhauses are often held as impulse-giving for contemporary architecture and design, and an argument can certainly be made that in many regards they were... With Bauhaus Ecologies the Bauhaus Museum, Dessau, seek to explore the relationships between both the Bauhauses as institutions and individual Bauhäusler and the non-human environment, from a variety of varied perspectives including, and amongst others, natural philosophy, biocentrism or crystallography, across a wide range of creative genres, including the more avant-garde artistic practices of the 1920s such as photography and film in their various expressions, but also the long established practice of architecture in context of, for example, considerations on climate-responsive construction methods...